Key Approaches and Algorithms
The Laplacian Score
The Laplacian Score is an unsupervised method to evaluate the importance of features based on the structure of the data itself. This method relies on the concept of graph Laplacians to measure feature relevance.
Graph Laplacians
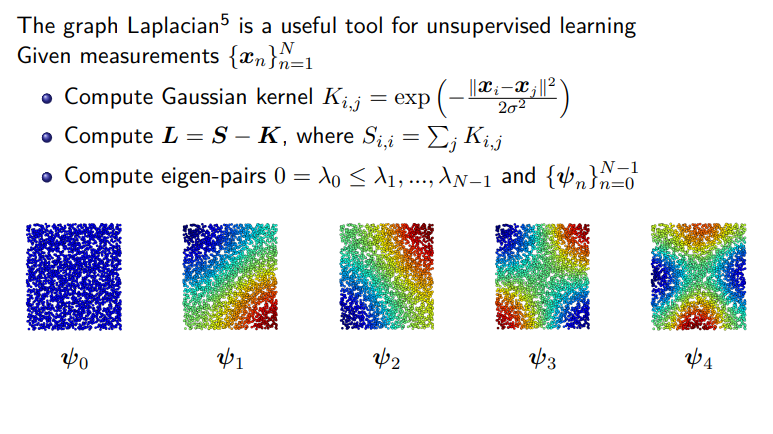
Graph Laplacians are matrix representations that capture the similarity between data points in a dataset. To define a graph Laplacian, we begin with a kernel matrix K, which is constructed using the Gaussian kernel.
where K_i,j is the similarity between data points x_i and x_j, and σ_b is a bandwidth parameter that can be chosen based on the dataset.
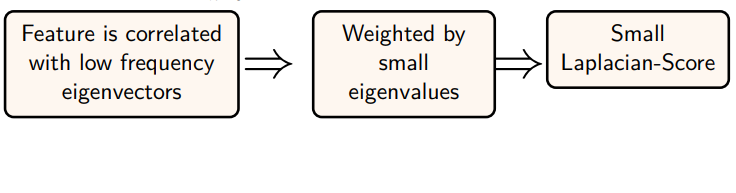
Laplacian Score
The Laplacian Score (LS) is an unsupervised feature selection metric that leverages the eigenvectors of the graph Laplacian matrix.
The score is minimized when the feature vector aligns well with the subspace formed by the smallest eigenvectors of L_un, indicating that the feature preserves the data’s local structure.
Eigenvectors corresponding to smaller eigenvalues of the graph Laplacian are associated with slowly varying features across the graph, which are considered to capture the intrinsic structure of the data, such as clusters.
In summary, features with the smallest Laplacian Scores are selected as they are most indicative of the underlying structure of the data.